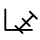La yod (𐤉) es la décima letra del alfabeto fenicio. Representaba el sonido palatal sonoro y fricativo transliterado como /j/.[1] De esta letra derivan la yud siríaca (ܝ), la yod hebrea (י), la yāʾ árabe (ي), la iota (Ι) griega, las I y J latinas y las І, Ї y Ј cirílicas.
Debido a la pronunciación semivocálica de esta letra, da su nombre al fenómeno lingüístico yod.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:12 430
-
canaanite-phoenician language: part 1 of punic inscriptions
Transcription
Historia
Literalmente significa «mano» o «brazo» y probablemente deriva de un glifo con el mismo significado.[2] De hecho, yod (יד) en hebreo y yad (يد) en árabe significan ambos «mano». El glifo podría estar últimamente relacionado con el jeroglífico de «mano».
El término yod se utiliza a menudo para referirse al sonido del habla [ j ], una aproximante palatina, incluso en discusiones sobre lenguas no escritas en abjads semíticos, como en fenómenos fonológicos como el inglés " yod-dropping ".
| Egipcio | Protosinaítico | Fenicio |
|---|---|---|
| 𓂣 | 𐤉 |
Evolución
| Fenicio | Púnico | Arameo | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imperial | Nabateo | Hatreo | Palmireno | ||
 |
 |
||||
Descendientes
Alfabeto árabe

La letra ي se llama yāʼ (يَاء). Su forma es diferente según su posición en la palabra:
| Posición | Aislada | Final | Media | Inicial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forma: | ی | ـی | ـیـ | یـ |
Se pronuncia como una aproximante palatal /j/, normalmente al principio de las palabras delante de vocales cortas o largas. Además puede sonar como una /i/ o una /e/ largas.
Como vocal, yāʾ puede servir como el "asiento" del hamza : ئ
Una forma similar pero distinta de yāʾ es ʾalif maqṣūrah ( أَلِف مَقْصُورَة) " alif limitado/restringido", con la forma ى. Indica una /aː/ larga final.
Alfabeto hebreo
En hebreo su nombre es יוֹד[3][4], coloquialmente יוּד. Representa una aproximante palatal ([j]). Como mater lectionis, representa la vocal [i]. Al final de palabras con vocal o cuando está marcado con un sheva naj, representa la formación de un diptongo, como /ei/ , /ai/ u /oi/.
Alfabeto siríaco
| Madnḫaya | Serṭo | Esṭrangela | Unicode |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
ܝ |
| Yod | Yud | Yod | yōḏ |
En alfabeto siríaco, la décima letra se llama, en siríaco clásico, ܝܘܕ - yōḏ. El valor numérico de la yōḏ es 10.
| Sonido principal principal | Mater lectionis |
|---|---|
| J | I |
El sonido principal de esta letra es /j/, pero la letra también se puede usar para representar el sonido vocálico /i/. Cuando la yōḏ va después de una rvaṣa, se lee solo una /e/, es decir, que la yōḏ no se lee.[5]
Unicode
| Carácter | ܝ | ࠉ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode | SYRIAC LETTER YUDH | SAMARITAN LETTER YUT | ||
| Codificación | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 1821 | U+071D | 2057 | U+0809 |
| UTF-8 | 220 157 | DC 9D | 224 160 137 | E0 A0 89 |
| Ref. numérica | ܝ | ܝ | ࠉ | ࠉ |
| Carácter | 𐎊 | 𐡉 | 𐤉 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode | UGARITIC LETTER YOD | IMPERIAL ARAMAIC LETTER YODH | PHOENICIAN LETTER YOD | |||
| Codificación | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 66442 | U+1038A | 67657 | U+10849 | 67849 | U+10909 |
| UTF-8 | 240 144 142 138 | F0 90 8E 8A | 240 144 161 137 | F0 90 A1 89 | 240 144 164 137 | F0 90 A4 89 |
| Ref. numérica | 𐎊 | 𐎊 | 𐡉 | 𐡉 | 𐤉 | 𐤉 |
Véase también
Referencias
- ↑ Krahmalkov, Charles R. (2001). «2. The alphabet, orthography and phonology». A Phoenician-Punic Grammar. Leiden; Boston; Köln: Brill. p. 20-21.
- ↑ Jensen, Hans (1969). Sign, Symbol, and Script. Nueva York: G.P. Putman's Sons. p. 262-263.
- ↑ «Morfix.mako.co.il». Archivado desde el original el 21 de julio de 2011. Consultado el 27 de noviembre de 2023.
- ↑ Fileformat.info
- ↑ Акопян, Арман (2010). Классический сирийский язык. Moscú: АСТ-Пресс. p. 23-24.